HSP90: Isoforms
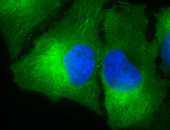
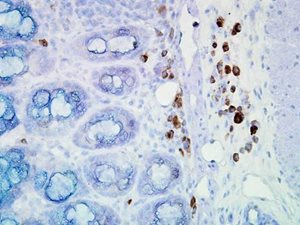 IHC staining of inflammatory cells in mouse colon tissue, using Anti-Hsp90 (clone: D7A)
IHC staining of inflammatory cells in mouse colon tissue, using Anti-Hsp90 (clone: D7A)
The HSP90 proteins are ubiquitous and highly conserved molecular chaperones present from bacteria to mammals. HSP90 proteins can be found in the cytosol, ER, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and the nucleus 1, 2, 3. Eubacteria express a single Hsp90 homolog, referred to as HtpG (high-temperature protein G) which is absent in Archaebacteria with the exception of Methanosarcina mazei who possesses a gene that is well aligned with the bacterial htpG 35, 36. Table 2 enumerates the most common members of the HSP90 family. All eukaryotes have several HSP90-encoding genes leading to the expression of compartment-specific isoforms fulfilling organelle-specific functions.
The human HSP90/HSPC family comprises 5 gene products differing from each other by expression level, subcellular location and amino acid constitution (Table 2). The two major cytosolic HSP90s cover the inducible Hsp90α1 (Hsp90AA1, HspC1) and the constitutive Hsp90β (Hsp90AB1, HspC3) resulting from a gene duplication about half a billion years ago 28. The HSP90AA1 gene is conserved in chimpanzee, Rhesus monkey, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish, A. thaliana, rice, and frog. 84 organisms have orthologs with the human HSP90AA1 gene. The HSP90AB1 gene is conserved in chimpanzee, Rhesus monkey, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish, fruit fly, mosquito, C. elegans, S. cerevisiae, K. lactis, E. gossypii, S. pombe, M. oryzae, N. crassa, A. thaliana, rice, and frog. 80 organisms have orthologs with the human HSP90AB1 gene.
Hsp90α2 (HspAA2, HspC2) represents a putative shorter isoform of Hsp90α1 of 343 amino acids which was originally classified as a pseudogene. Nowadays, the existence of this protein is supported by unambiguous mass spectrometry evidence 37. Hsp90α2 may be implicated in promoting the maturation, structural maintenance and proper regulation of specific target proteins.
Grp94 (HspC4, Hsp90B1) constitutes the ER paralog of Hsp90 which arose by a gene duplication event very early in the evolution of eukaryotic cells 38, 39. Grp94 is present in all eukaryotes with the exception of fungi that have most probably lost it 38. While Hsp90α and Hsp90β can be induced by elevated temperature, Grp94 is glucose-regulated and induced by glucose starvation 1. It participates in protein folding and assembly, protein secretion, apoptosis protection, and mediating immunogenicity in tumour and virally infected cells 39, 40. The HSP90B1 gene is conserved in chimpanzee, Rhesus monkey, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish, fruit fly, mosquito, C. elegans, A. thaliana, rice, and frog. 90 organisms have orthologs with human gene HSP90B1.
Trap-1 (HspC5, Hsp90L) is located to mitochondria and contains a mitochondrial localization sequence at the N-terminus 2. The TRAP1 gene is conserved in chimpanzee, Rhesus monkey, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish, fruit fly, mosquito, C. elegans, and frog. 89 organisms have orthologs with human gene TRAP1. Although Trap-1 does not form stable complexes with the classic Hsp90 co-chaperones p23 and Hop (p60), it binds ATP and exhibits ATPase activity that is inhibited by both, geldanamycin and radicicol thereby ensuring its position among the HSP90 family 2. From these observations it can be postulated that Trap-1 functions differently than the other HSP90 family members 2. These functional discrepancies might be related to the lack of the C-terminal M-D-E-E-V motif 26, 41, 42. According to Chen and colleagues, Trap-1 appears to represent a distant relative of Hsp90 due to its structural and functional similarity 42. A genome-wide analysis of the human HSP90 family revealed that mitochondrial Trap-1 and cytosolic/ER-specific isoforms are well supported paralogous groups 26. Trap-1 is most closely related to eubacterial HtpG because both harbour a very short charged linker region and lack the C-terminal M-E-E-V-D motif suggesting that Trap-1 originated from a HtpG-like ancestor 2, 36. Unlike all other HSP90 family members, Trap-1 possesses a unique L-X-C-X-E motif which was found to be important for binding to the simian virus 40 T-antigen-binding domain of hypophosphorylated retinoblastoma protein (Rb) 43.